Adrenergic Drugs Generally Produce Which of the Following Responses
A nurse administers propranolol hydrochloride Inderal. CNSwakefulness quick reaction to stimuli quickened reflexes PNSrelaxation of the smooth muscles of the.
Adrenergic Drugs Basicmedical Key
Adrenergic ligands also arrive at the synapse via the circulatory system.

. These drugs bind to more of the adrenergic receptors when administered at higher doses ie can lose selectivity. Adrenergic Drugs q Adrenergic receptors are divided into two major types according to drug. Relaxation of smooth muscles of the bronchi e.
Tyrosine Dopamine. Adrenergic Drugs q Adrenergic receptors are divided into two major types according to drug potency on the receptors q Alpha- α- adrenergic receptors when activated generally produce excitatory responses q Beta- β- adrenergic receptors when activated generally produce inhibitory responses. Adrenergic drugs such as metaraminol Aramine isoproterenol Isuprel and ephedrine are synthetic adrenergic drugs.
The synthesis of adrenergics follows the pathway below adrenergic means pertaining to systems that respond to adrenalin. ACTIONS Generally adrenergic drugs produce one or more of the following responses in varying degrees. Increased heart rate b.
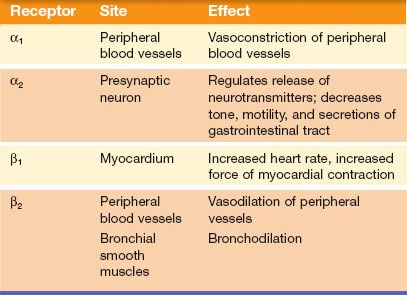
Adrenergic drugs generally produce which of the following responses. Adrenergic drugs that produce or inhibitthese effects are known as sympathomimetic agents and sympatholytic agents respectively. The smooth muscles of the bronchioles and of some blood vessels however are.
Causes the release of the catecholamine from the storage sites vesicles in the nerve endings--then binds to the receptors causes a physiologic response. This adrenergic receptor subtype is expressed on vascular smooth muscle at sites some distance away from sympathetic nerve terminals and produces vasoconstrictor responses when stimulated by circulating catecholamines such as epinephrine. Many of the beta-adrenergic blockers are nonselective blocking both beta1 and beta2 receptors.
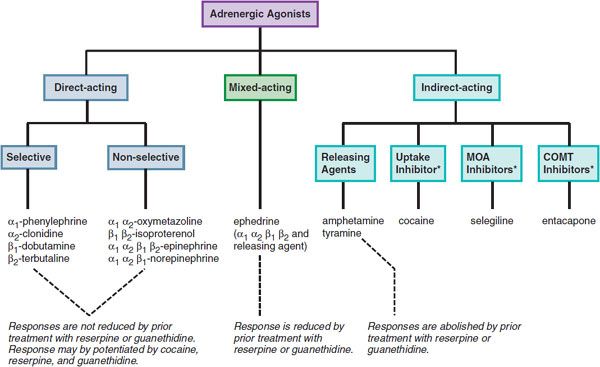
The nurse would anticipate administering drugs that generally block all adrenergic receptor sites to treat a. Sympathetic nervous system stimulation also results in bronchodilation dilated pupils and decreased gastrointestinal mobility depending upon which receptors are stimulated. Adrenergic agonists are autonomic nervous system drugs that stimulate the adrenergic receptors of the sympathetic nervous system SNS either directly by reacting with receptor sites or indirectly by increasing norepinephrine levels.
Thus they constrict blood vesselsvasoconstriction which increases blood pressure and accelerate the rate and force of contractions of the heart. Dopamine binds to the alpha-1 alpha 2 beta-1 receptors and also dopamine receptors. Adrenergic beta-antagonists are used for treatment of hypertension cardiac arrhythmias angina pectoris glaucoma migraine headaches and anxiety.
Can precipitate a hypertensive crisis. The termination of norepinephrine NE is due primarily to reuptake into the nerve ending. Increased heart rate is one of the effects of adrenergic drugs.
Epinephrine binds to all of the adrenergic receptors. Centrally acting antiadrenergic agents inhibit the stimulation of the central nervous system alpha-adrenergic receptors and decrease sympathetic stimulation to the blood vessels and the heart. When activated by NE further release of the neurotransmitter is inhibited.
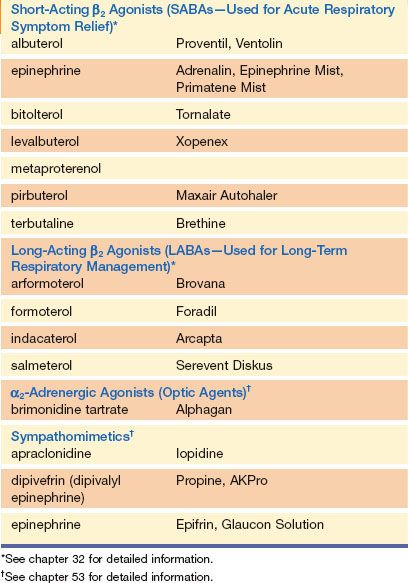
Body are used in medicine. The following are key clinical indications of various adrenergic drugs. Adrenergic crises occur primarily in the presence of a pheochromocytoma.
An adrenergic agonist is also called a sympathomimetic because it stimulates the effects of SNS. However they can also occur after acute withdrawal of clonidine or possibly methyldopa145 In the past adrenergic crises also were seen after the ingestion of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in combination with tyrosine-rich food. The three main catacholamines chatecol is ortho-dihydroxybenzene are epinephrine EP norepinephrine NE and dopamine DA.
Note that adrenalin and epinephrine are the same molecule as are noradrenalin and NE. Its pharmacological effects depend on the concentration and the type and number of available receptors Generally it has more affinity for β receptors. Decreased pulse rate and bronchoconstriction.
The response would be. Epinepherine adrenaline acts strongly on both α and β adrenoceptors. These drugs inhibit monoamine oxidase and are used as antidepressants in psychiatric practice.
Adrenergic blocking drugs because of their clinical effects are also known as a. Both directly stimulates the receptor by binding to it indirectly stimulates the receptor by causing. They block the release and action of catecholamines epinephrine norepinephrine dopamine which are released in response to stress.
Binds directly to the receptor. These include epinephrine E and norepinephrine NE secreted by the adrenal medulla or adrenergic drugs D. A host of physiological and metabolic responses follows stimulation of sympathetic nerves in mammals is usually mediated by the neurotransmitter norepinephrine.
So at lower concentration β effect predominates. -Adrenergic Receptors Type Distribution Receptor Transduction Agonist. Increased use of glucose c.
One of the first beta-adrenergic blockers beta blocker was propranolol Inderal. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Beta Blockers are generally safe overdose can produce symptoms of. Adrenergic stimulationby epinephrine in the blood and by norepinephrine released from sympathetic nerve endingshas both excitatory and inhibitory effectsThe heart dilatory muscles of the iris and the smooth muscles of many blood vessels are stimulated to contract.
Action of Adrenergic Drugs. A side effect that is not clearly understood is that these drugs can also produce hypotension.

Adrenergic Drugs Adrenergic Receptors Are Divided Into Two Major Types According To Drug Potency On The Receptors Alpha A Adrenergic Receptors Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment